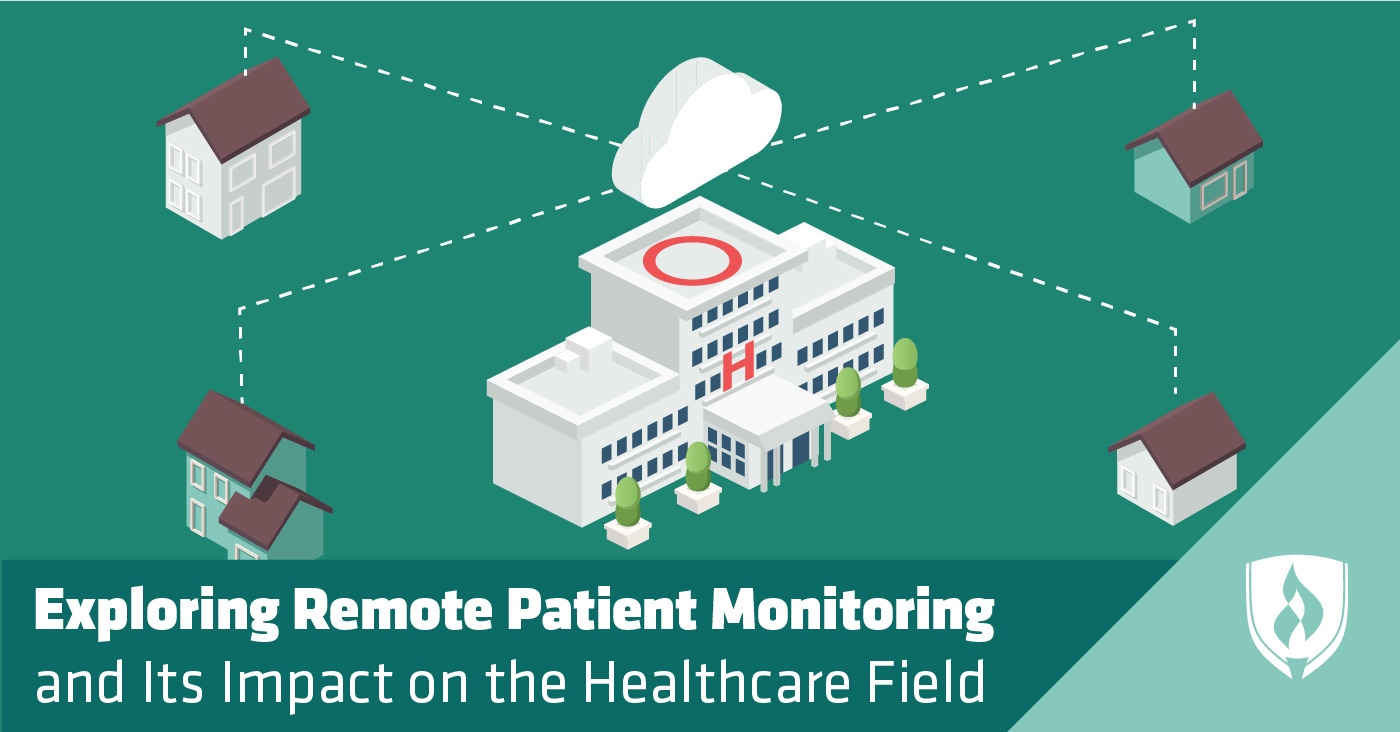
Technological innovation has steadily changed the face of modern medicine over the years. One of the major shifts is the rise of remote patient monitoring to improve health outcomes and increase access to medical care.
Many Americans have relied on the technology on their smartphones, fitness trackers or smart watches to provide health data in their day-to-day lives. Using technology to collect and analyze diet, exercise, and basic vital signs has been a part of many people’s personal efforts to improve their health and wellness. Healthcare providers have also incorporated these technologies to provide better care based on a larger and more accurate portrait of a patient’s health.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further influenced healthcare providers’ use of remote patient monitoring. As traditional healthcare sites such as clinics and hospitals become potentially dangerous vectors of transmission, healthcare providers increasingly rely on telehealth services (healthcare services provided remotely) to give medical care—and remote patient monitoring is a powerful tool for healthcare providers practicing telemedicine.
What is remote patient monitoring?
So what is remote patient monitoring? On the most basic level, remote patient monitoring is any method of recording a patient’s health data outside of a traditional clinical or hospital setting and sending that data to qualified healthcare providers.
The origin of remote patient monitoring as practiced today is—surprisingly—the space program. In the 1960s, NASA doctors and scientists needed to monitor and study astronauts as they went into outer space.1 The technology used to remotely monitor astronaut health was then put to use below the clouds—starting a slow but steady march.
By the 1980s collecting x-rays and EKG data and transmitting them through telephone wires had become routine practice for Earth-bound patients as well. In the 1990s, the internet opened up an entirely new avenue for collecting and transmitting health data.
What are the most common tools in remote patient monitoring?
Most Americans already own one of the most high-tech and popular tools for remote patient monitoring, a smart phone. Devices such as a blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, and glucometers can all be used to collect health data which is then stored, analyzed, and transmitted to healthcare providers through a smartphone. Other technology can be used such as tablets, smart watches, and other devices.
You may already use a health and wellness app on your phone. The rising accessibility of complex technology allows people interested in managing and improving their health more tools to accurately measure and analyze their progress. These personal applications use the same tools as remote patient monitoring, the key difference being that they do not typically send your data to a healthcare provider for analysis and treatment.
Who uses remote patient monitoring?
Many methods of remote patient monitoring are designed to address chronic conditions. Individuals with chronic heart conditions can anticipate changes in their health using remote patient monitoring. Patients managing diabetes also rely on remote patient monitoring to keep track of blood pressure, weight, and blood glucose levels.
Remote patient monitoring is also an important tool for providing care and ensuring the safety of individuals dealing with dementia or high fall risk. Sensors on mobility devices can detect dangerous falls and movement changes and alert healthcare providers and caretakers.
During times of pandemic, remote patient monitoring technology can help providers keep up with regular patient check-ups while minimizing the risk of exposure. But even beyond extreme circumstances, these tools can be a boon for those without easy access to transportation or live in areas that are far away from healthcare provider.
What are the actual impacts of remote patient monitoring?
There is some debate around the impact of remote patient monitoring, though a review of research conducted between 2000-2018 suggests remote patient monitoring and other telemedicine initiatives have been generally positive.2 That finding makes sense at face value—increasing patient access and making it easier for healthcare questions and concerns to be addressed is a clear positive. That said, telemedicine and remote patient monitoring do rely on patients taking an active role in their healthcare. Patients need instruction on how to properly utilize these tools and, like with traditional visits, need to follow through with the advice or orders of their care teams to be effective.
There’s also the potential for saving on healthcare costs through early detection and preventative treatments. Instead of waiting for an unchecked health issue to progress to something more serious that could require an emergency room visit, providers may have the opportunity to intervene with earlier, less expensive treatments.
What is the future of remote patient monitoring?
For researchers, healthcare providers, and patients, remote patient monitoring has been an exciting area of development within medicine. Remote patient monitoring has the potential to increase the quality of healthcare patients receive and allow them to spend more time in their homes rather than in a clinic or hospital setting.
Continued technological innovation and increased access to technology indicates a bright future of remote patient monitoring. Telemedicine is an important tool for providing care to patients in rural areas, with disabilities, and other limitations that keep them from having access to in person health services. Remote patient monitoring is an essential tool to providing effective telemedicine.
Embracing healthcare technology
Medicine is a dynamic and ever evolving field. The role of technology in modern medicine has allowed for breakthroughs in the quality of care healthcare workers are able to provide. Take a look at 5 Ways Technology in Healthcare Is Transforming the Way We Approach Medical Treatment.
Related Articles:
1National Aeronautics and Space Administration, A Brief History of NASA’s Contributions to Telemedicine [accessed June, 2020] https://www.nasa.gov/content/a-brief-history-of-nasa-s-contributions-to-telemedicine
2American Telemedicine Association, Remote Patient Monitoring: A Systematic Review, [accessed June, 2020] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31314689/

-(1).png)